本文介绍 Divide and Conquer(分而治之) 的一种典型算法,FFT(快速傅里叶变换)。
DFT
DFT:$X[k] = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} x[n] e^{-j \frac{2 \pi k}{N} n}, k = 0, 1, 2, …, N-1$
- for each k: N complex mults, N-1 complex adds
- $e^{-j \frac{2 \pi k}{N} n}$ 预计算并保存在计算机中
- $O(N^2)$ computations for direct DFT $\Longrightarrow$ $O(N log_2 N)$ for FFT
FFT 算法原理
做出如下定义:$W_N = e^{-j \frac{2 \pi}{N}}$,则:$W_N^{kn} = e^{-j \frac{2 \pi k}{N} n}$,具有如下性质:
- $W_N^{kN} = e^{-j 2 \pi k } = 1$
- 复共轭对称:$W_N^{k(N-n)} = W_N^{-kn)} = (W_N^{kn})^{*}$
- 周期性:$W_N^{kn} = W_N^{k(N+n))} = W_N^{(k+N)n}$
假设 $N = 2^m$,separate $x[n]$ into even and odd-indexed subsequences
$ X[k] = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} x[n] W_N^{kn} = \sum_{n \in even} x[n] W_N^{kr} + \sum_{n \in odd} x[n] W_N^{kr} $
$ X[k] = \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r] W_N^{k 2r} + \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r+1] W_N^{k(2r+1)} $
$ = \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r] (W_N^2)^{kr} + W_N^k \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r+1] (W_N^2)^{kr} $
But:$W_N^2 = e^{-j \frac{2 \pi}{N} 2} = e^{-j \frac{2 \pi}{\frac{N}{2}}} = W_{\frac{N}{2}}$
$ X[k] = \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r] W_{\frac{N}{2}}^{kr} + W_N^k \sum_{r=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} x[2r+1] W_{\frac{N}{2}}^{kr} $
$ = X_e[k] + W_N^k X_o[k]$
其中,$X_e[k]$:N/2 DFT of even samples,$X_o[k]$:N/2 DFT of odd samples,$X[k] \Rightarrow$ sum of 2 N/2 point DFTs
举$N=8$作为一个例子,根据上述的思路进行一次二分,如下图:
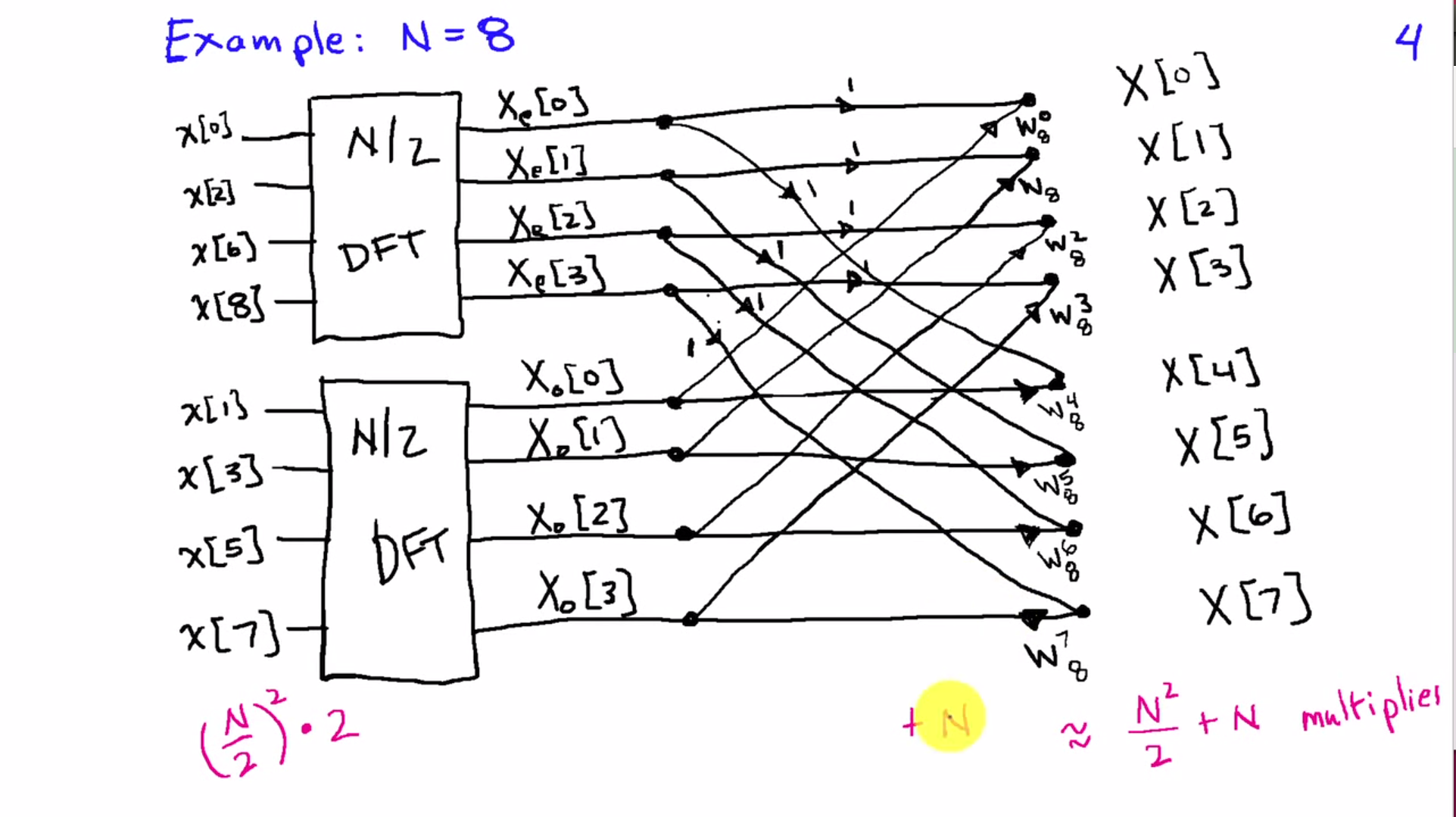
左边按照普通的 DFT 计算($O(n^2)$的时间复杂度)得到$x_e[0…3]$和$x_o[0…3]$,需要$(\frac{N}{2})^2·2$ 次乘法;$W_8^{0…7}$ 的预计算需要 $N$ 次乘法;最后的 $X[0…7]$ 的计算每一项都需要一次乘法,总共需要 $N$ 次乘法。故通过一次二分得出的计算复杂度估计为 $\frac{N^2}{2} + N$
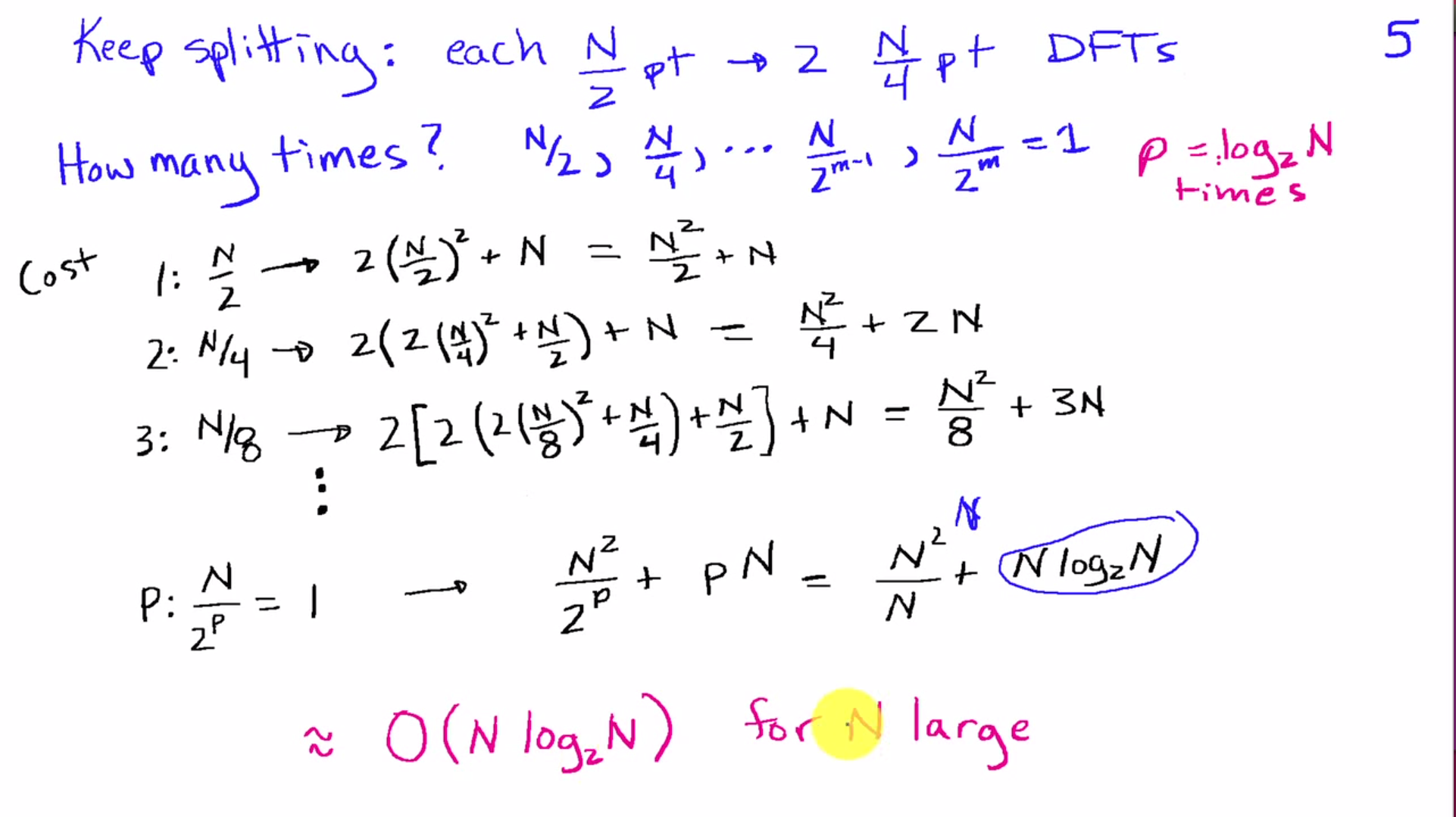
按照这种思路,继续二分下去(如下图),得到 FFT 算法的最终时间复杂度:$O(N log_2 N)$
.png)
FFT算法实现
- 源代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212// FFT.cpp
// define a complex structure
struct Complex_ {
double real;
double imagin;
};
typedef struct Complex_ Complex;
// define complex computation: add/subtract/multiply
void Complex_Add(Complex* src1, Complex* src2, Complex* dst){
dst->real = src1->real + src2->real;
dst->imagin = src1->imagin + src2->imagin;
}
void Complex_Sub(Complex* src1, Complex* src2, Complex* dst){
dst->real = src1->real - src2->real;
dst->imagin = src1->imagin - src2->imagin;
}
void Complex_Multiply(Complex* src1, Complex* src2, Complex* dst){
double r1 = 0.0, r2 = 0.0;
double i1 = 0.0, i2 = 0.0;
r1 = src1->real;
i1 = src1->imagin;
r2 = src2->real;
i2 = src2->imagin;
dst->real = r1*r2 - i1*i2;
dst->imagin = i1*r2 + r1*i2;
}
// get W_N^k
void getWN(double k, double N, Complex* dst){
double x = 2.0*M_PI*k/N;
dst->real = cos(x);
dst->imagin = -sin(x);
}
// input generator
void input_generator(double* data, int n){
srand((int)time(0));
for(int i=0; i<SIZE; i++){
data[i] = rand()%VALUE_MAX;
printf("%lf\n",data[i]);
}
}
/*
* normal DFT algorithm, with O(n^2) complexity
*/
void DFT(double* src, Complex* dst, int size) {
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
// 2 cycle, each with step of 1, size n, so O(n*n)
for(int m=0; m<size; m++){
double real = 0.0;
double imagin = 0.0;
for(int n=0; n<size; n++){
double x = M_PI*2*m*n;
real += src[n]*cos(x/size);
imagin += src[n]*(-sin(x/size));
}
dst[m].imagin = imagin;
dst[m].real = real;
if(imagin >= 0.0)
printf("%lf+%lfj\n", real, imagin);
else
printf("%lf%lfj\n", real, imagin);
}
end = clock();
printf("DFT use time :%lf for Datasize of:%d\n",(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC, size);
}
void IDFT(Complex* src, Complex* dst, int size) {
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
for(int m=0; m<size; m++) {
double real = 0.0;
double imagin = 0.0;
for(int n=0; n<size; n++) {
double x = M_PI*2*m*n/size;
real += src[n].real*cos(x)-src[n].imagin*sin(x);
imagin += src[n].real*sin(x)+src[n].imagin*cos(x);
}
real /= SIZE;
imagin /= SIZE;
if(dst != NULL){
dst[m].real = real;
dst[m].imagin = imagin;
}
if(imagin >= 0.0)
printf("%lf+%lfj\n", real, imagin);
else
printf("%lf%lfj\n", real, imagin);
}
end=clock();
printf("IDFT use time :%lfs for Datasize of:%d\n", (double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC,size);
}
// define FFT initialization data, remapping
int FFT_remap(double* src, int N) {
if(N == 1)
return 0;
double* temp = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*N);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
if(i%2==0)
temp[i/2] = src[i];
else
temp[(N+i)/2] = src[i];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
src[i] = temp[i];
free(temp);
FFT_remap(src, N/2);
FFT_remap(src+N/2, N/2);
return 1;
}
void FFT(double* src, Complex* dst, int N){
FFT_remap(src, N);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
printf("%lf\n", src[i]);
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
int n = N;
int k = 0;
// get number of stage
int stage = 0;
while(n /= 2) {
stage++;
}
n = stage;
if(N != (1<<n))
exit(0);
Complex* src_complex = (Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex)*N);
if(src_complex == NULL)
exit(0);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
src_complex[i].real = src[i];
src_complex[i].imagin = 0;
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
k = 0;
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if((j/(1<<i))%2 == 1) {
Complex WNk;
getWN(k, N, &WNk);
Complex_Multiply(&src_complex[j], &WNk, &src_complex[j]);
k += 1<<(k-i-1);
Complex temp;
int neighbour = j-(1<<(i));
temp.real = src_complex[neighbour].real;
temp.imagin = src_complex[neighbour].imagin;
Complex_Add(&temp, &src_complex[j], &src_complex[neighbour]);
Complex_Sub(&temp, &src_complex[j], &src_complex[j]);
}
else
k = 0;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
if(src_complex[i].imagin >= 0.0) {
printf("%lf+%lfj\n", src_complex[i].real, src_complex[i].imagin);
}
else
printf("%lf%lfj\n", src_complex[i].real, src_complex[i].imagin);
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
dst[i].imagin = src_complex[i].imagin;
dst[i].real = src_complex[i].real;
}
end = clock();
printf("FFT use time :%lfs for Datasize of:%d\n",(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC, N);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
double input[SIZE];
Complex dst[SIZE];
input_generator(input, SIZE);
printf("\n\n");
DFT(input, dst, SIZE);
printf("\n\n");
FFT(input, dst, SIZE);
return 0;
}
- 编译构建
1
gcc -o FFT FFT.cpp -lm
- 测试结果
DFT use time :33.963164 for Datasize of:16384
FFT use time :0.090624s for Datasize of:16384